Optom Posts
Diabetic Diet
3rd April, 2014Diabetic Diet The glycemic load (GL) of food is a number that estimates how much the food will raise a person's blood glucose level after eating it. Glycemic load estimates the impact of carbohydrate consumption using the [...]
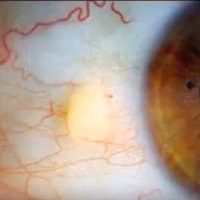
Pinguecula - yellow-white deposits on White of eye
2nd April, 2014Pingueculae are found more often on the nasal side of the conjunctiva. While most pingueculae are found over the age of 40, they are not uncommon in 20 and 30 years old adults who spend significant time in the sun.
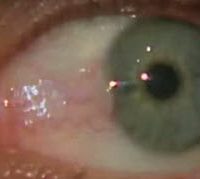
Pterygium - Growth on white of the Eye
2nd April, 2014Pterygium in the conjunctiva is characterized by elastotic degeneration of collagen (actinic elastosis) and fibro vascular proliferation.
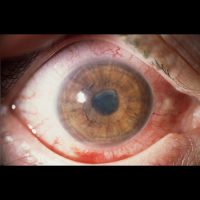
Anterior Uveitis or Iritis
31st March, 2014Uveitis Painful red eye: requires an urgent referral and thorough examination by an Ophthalmologist or Optometrist and urgent treatment to control the inflammation.
Hyperopia : Often called Long-Sighted
18th March, 2014Hyperopia,farsighted, Longsighted, or hypermetropia, is a defect when the eyeball is too short or the cornea too flat. This causes difficulty focusing on near objects, and in extreme cases a sufferer to be unable to focus on objects at any distance.
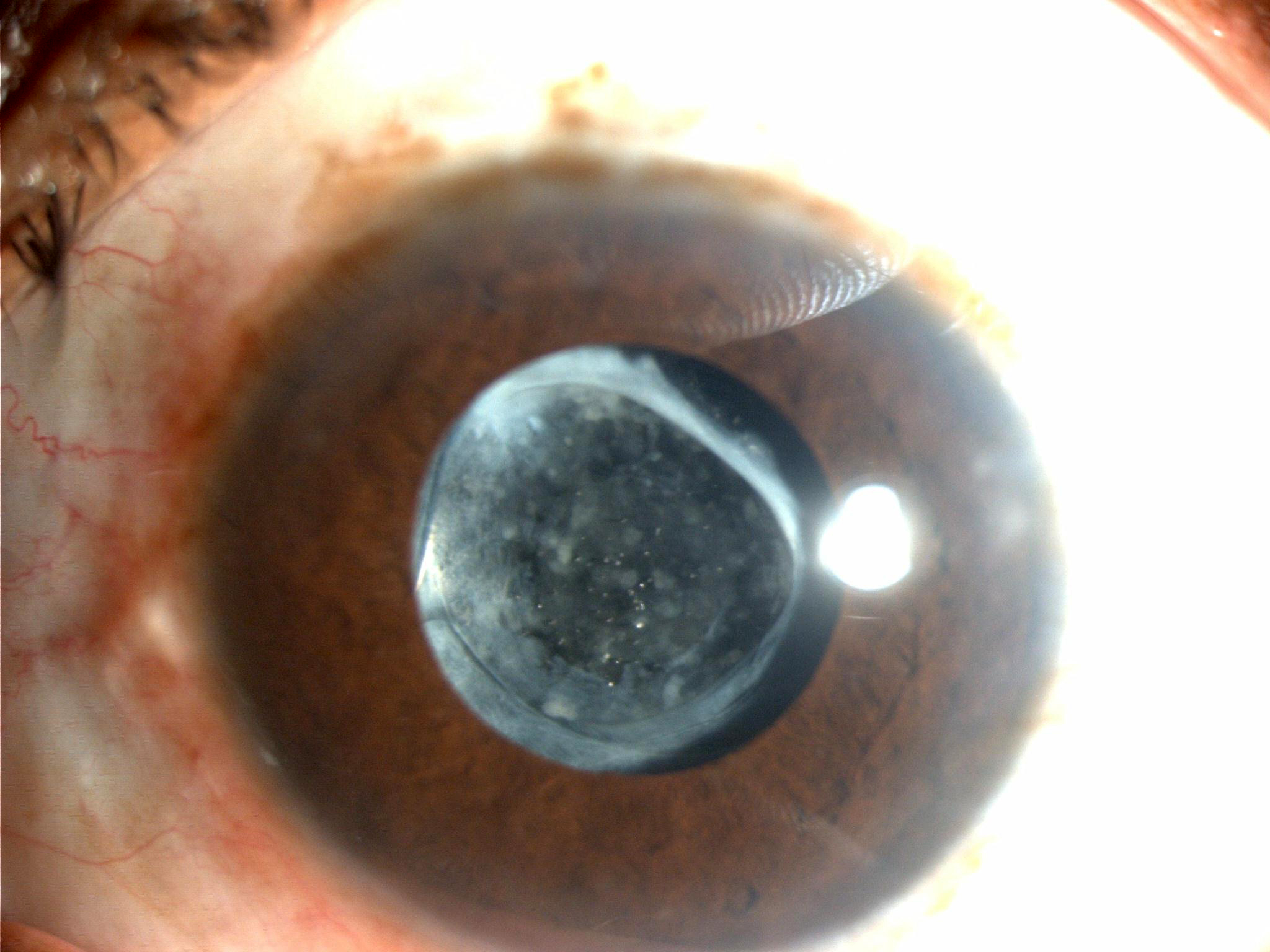
Yag Capsulotomy for Posterior Capsular Opacification
18th March, 2014posterior capsular opacification (PCO, also called an after-cataract). The posterior capsular cells undergo hyperplasia and cellular migration, showing up as a thickening and clouding of the posterior lens capsule (which is left behind when the [...]
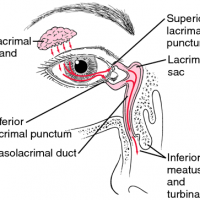
Syringing the Lacrimal Drainage System
4th March, 2014Syringe Tear ducts: Probing and Irrigation of the lacrimal drainage system to assess any lacrimal system obstruction in the case of persistant watery eyes
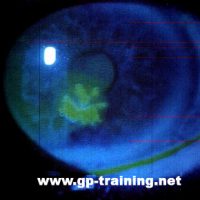
Herpes in the Eye - Herpes Simplex Keratitis
4th March, 2014Herpes viruses establish lifelong infections, and the virus cannot yet be eradicated from the body. Treatment usually involves general-purpose antiviral drugs that interfere with viral replication,
Herpes Zoster commonly known as Shingles
3rd March, 2014Shingles or herpes zoster is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a limited area on one side of the body (left or right), often in a stripe. The initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV) causes the acute, [...]
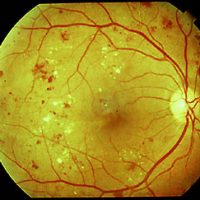
Retinal Neovascularization - Aftereffects of CRVO or Diabetes
25th February, 2014Intraretinal microvascular abnormalities (IRMA) are abnormalities of the blood vessels that supply the retina of the eye, a sign of diabetic retinopathy.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy - PDR
25th February, 2014As the Diabetic Retinopathy progresses, severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy enters an advanced, or proliferative (PDR), stage when blood vessels proliferate (i.e. grow).
Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome and Glaucoma
21st February, 2014pseudoexfoliation syndrome is tiny microscopic white or grey granular flakes which are clumps of proteins within the eye this can lead to Glaucoma
Retinal Detachment Surgery - Scleral Buckle and Vitrectomy
21st February, 2014Retinal detachments are usually caused by retinal tears, and a scleral buckle can be used to close the retinal break. The scleral buckle is secured around the eyeball under the conjunctiva. This moves the wall of the eye closer to the [...]
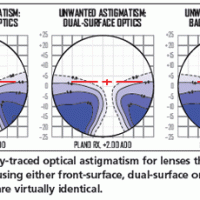
The Best Progressive Lenses - Personalised for You
20th February, 2014Custom designed Progressive or Multi Focal Lenses Graduated or Progresssive lenses made for you personally,diffferent head positions and indivual eye moments require personally desigened lenses
Rigid Gas Permeable Contact Lens - Care and maintanance
20th February, 2014RGP Lens also known as Gas Permeable Rigid lens. Rigid gas permeable lenses are rigid contact lenses made of oxygen-permeable polymers. Initially developed in the late 1970s, and through the 1980s and 1990s, they were an [...]
Soft Contact Lens Handling
14th February, 2014 Here's some way's to put in and remove your contact lenses; there is no CORRECT way do what works BUT KEEP IT CLEAN!!!! case and hands Gadgets are handy but your fingers attached and hopefully always there. Despite the comments on this [...]
Myopia - Near Vision is Good
13th February, 2014When you have Myopias The eyes focal is in front of the retina allowig close objects to be seen clearly but the distance is blurred.
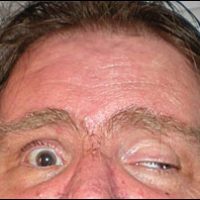
Cranial Nerve 3 - Controls 4 of 6 Extra-Ocular muscles
12th February, 2014The third cranial nerve innervates 4 of the 6 extra ocular muscles, if it is paralyzed the eye will turn down and out, on that side, often severe ptosis (droopy upper lid), often a dilated pupil and loss of near vision in young people
The Abducens Nerve - 6th Cranial Nerve Palsy
12th February, 2014Abducent nerve or 6th Cranial Nerve supplies the lateral rectus muscle If damaged the eye will not turn out
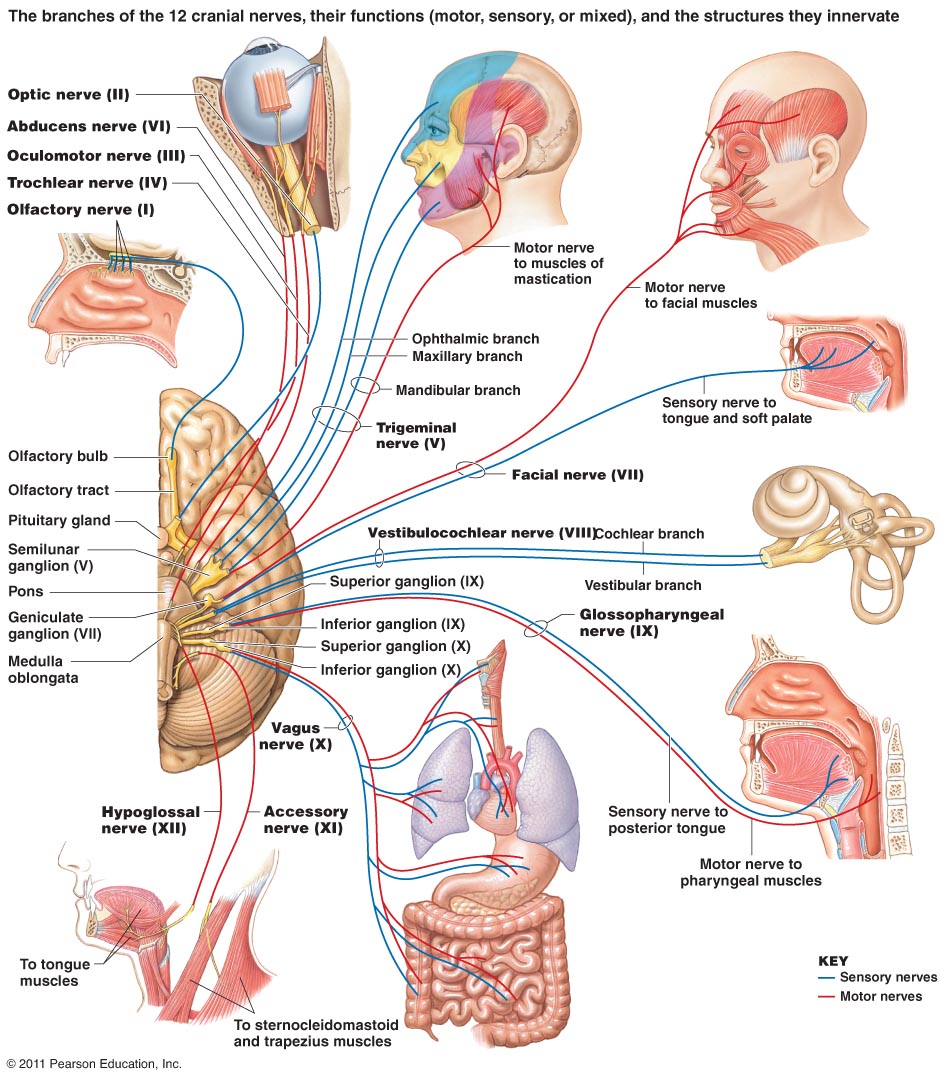
The Cranial Nerves - Sensory and Motor functions
11th February, 2014The cranial nerves control a large number of our social, sensory and motor functions this is a brief overview of their importance.