Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome and Glaucoma
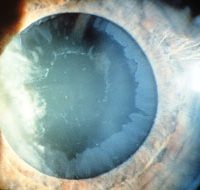
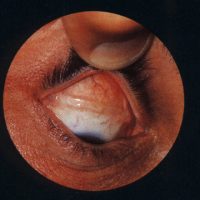
21 Feb 2014Pseudoexfoliation syndrome (PEX) is characterized by tiny microscopic white or grey granular flakes which are clumps of proteins within the eye which look somewhat like dandruff when seen through a microscope and which are released by cells.The [...]
Retinal detachments are usually caused by retinal tears, and a scleral buckle can be used to close the retinal break. The scleral buckle is secured around the eyeball under the conjunctiva. This moves the wall of the eye closer to the [...]
Custom designed Progressive or Multi Focal Lenses Graduated or Progresssive lenses made for you personally,diffferent head positions and indivual eye moments require personally desigened lenses
RGP Lens also known as Gas Permeable Rigid lens. Rigid gas permeable lenses are rigid contact lenses made of oxygen-permeable polymers. Initially developed in the late 1970s, and through the 1980s and 1990s, they were an [...]
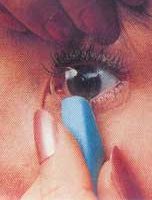
Soft Contact Lens Handling
14 Feb 2014 Here's some way's to put in and remove your contact lenses; there is no CORRECT way do what works BUT KEEP IT CLEAN!!!! case and hands Gadgets are handy but your fingers attached and hopefully always there. Despite the comments on this [...]
Myopia - Near Vision is Good
13 Feb 2014The Focus is in front of the retina allowig close objects to be seen clearly but the distance is blurred.
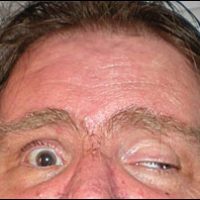
Third Cranial Nerve Palsy The third cranial nerve innervates 4 of the 6 extra ocular muscles, if it is paralyzed the eye will turn down and out, on that side, often severe ptosis (droopy upper lid), often a dilated pupil and loss of near vision in[...]
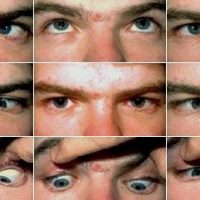
The Abducens Nerve - 6th Cranial Nerve Palsy
12 Feb 2014Abducent nerve or 6th Cranial Nerve supplies the lateral rectus muscle Sixth nerve palsy (the abducens nerve) is responsible for contracting the lateral rectus muscle to abduct (i.e., turn out) the eye. The inability of an eye to turn [...]
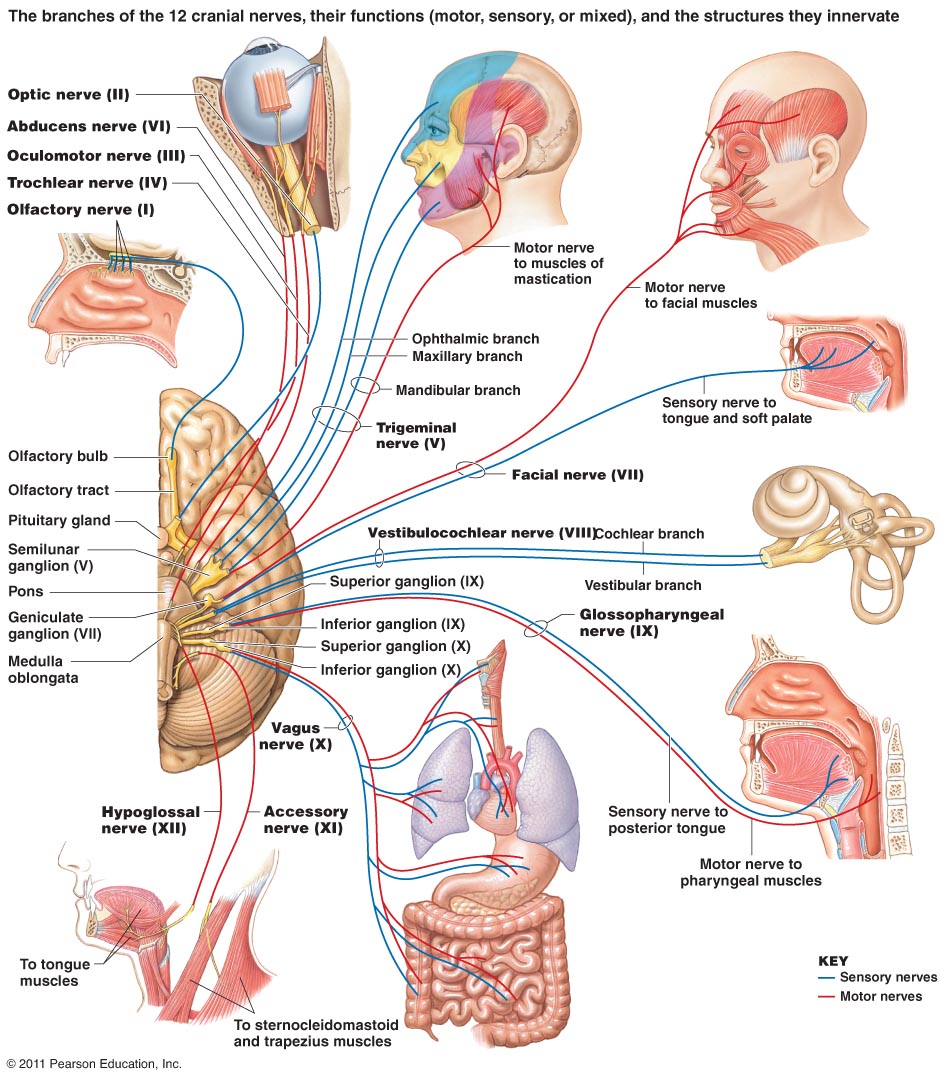
The Cranial Nerves - Sensory and Motor functions
11 Feb 2014The cranial nerves control a large number of our social, sensory and motor functions this is a brief overview of their importance. Cranial nerves emerge directly from the brain, in contrast to spinal nerves, which emerge from segments of the [...]
Visual Fields - Our Side Vison
11 Feb 2014In optometry and ophthalmology a visual field test is used to determine whether the visual field is affected by diseases that cause local scotoma (glaucoma) or a more extensive loss of vision (brain lesion) or even a reduction in sensitivity [...]
Location & Contact Details
© 2017 - 2024 Noel Templeton Optometrists